- Home
-
About
-
About
After more than 20 years of equipment manufacturers, a fullset of professional beverage machinery production linesprovide every customer with lifelong equipment services!
-

Company Profile

Company Culture

Certificate Honor

Factory Photos
-
-
Products
-
Products
Specializing in the production of food and beverage, beer, mineralwater and other mechanical equipment design and manufacturingthe whole line technology, the whole plant design planning, andinstallation and commissioning technology.
-
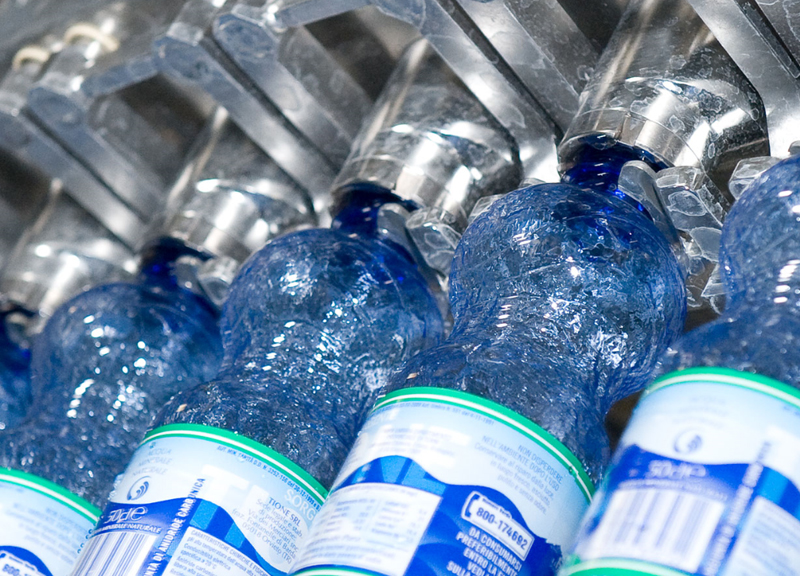

Filling Machine
Provide various series of bottled water, barreled water, fruit juice, carbonated drinks, alcohol, oil and other filling
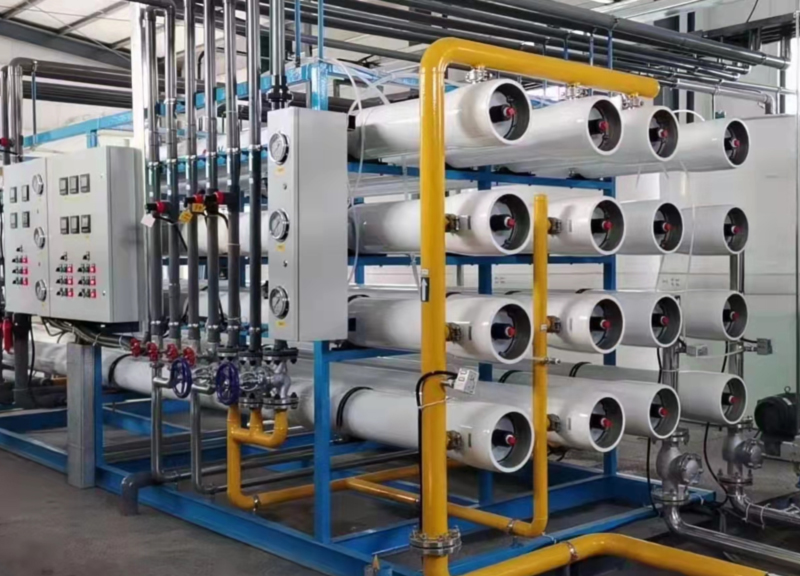

Filling Auxiliary Equipment
Provide filling auxiliary equipment, including water treatment equipment, beverage mixer, sterilizer, bottling machine and other equipment
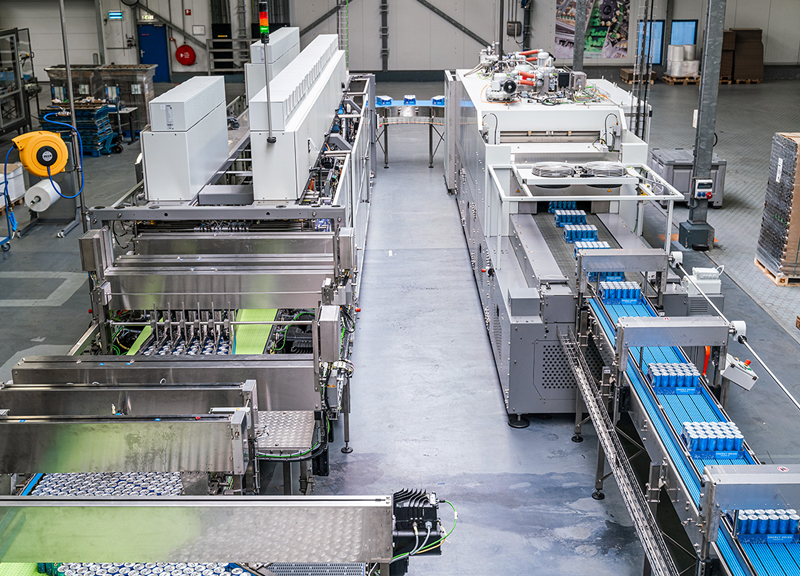

Packaging Machine
Provide packaging equipment, including labeling machine, labeling machine, film packaging machine, packaging machine and other series of equipment

Bottle Blowing Machine
Bottle blowing machine is a kind of equipment that can make plastic particles into hollow containers through blow molding process
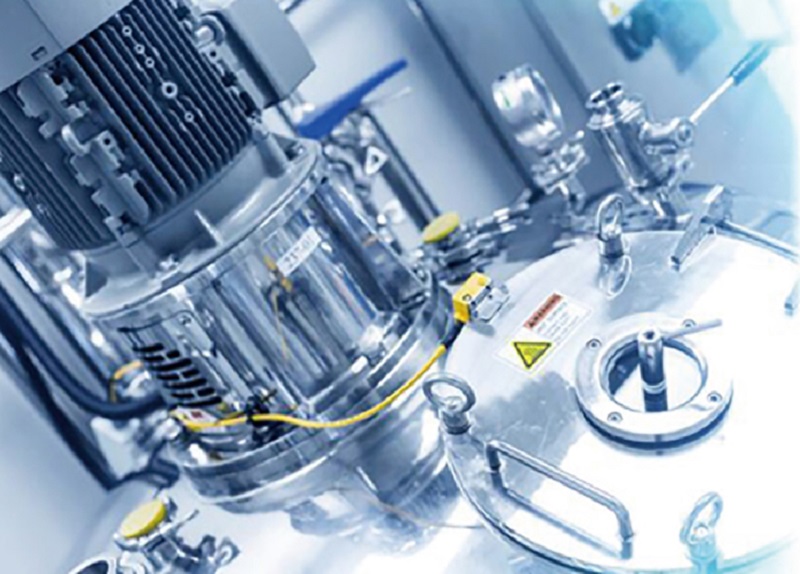

Fermentation Machine
Provide fermentation equipment such as probiotics and lactic acid bacteria
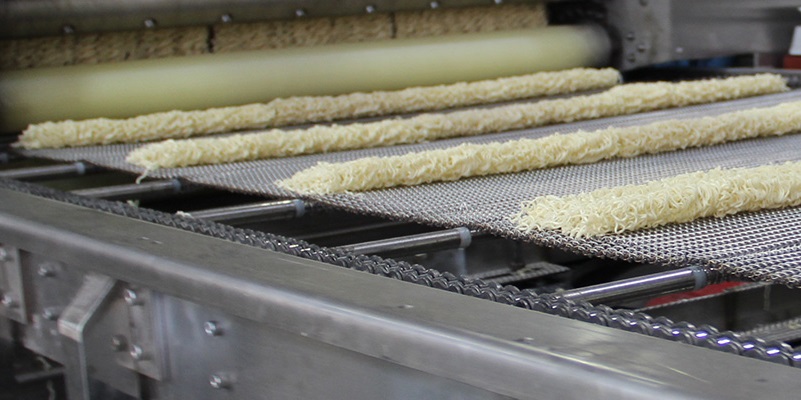

Noodles Machine
Provide various series of automatic noodle equipment
-
-
Industry
-
Industry
Focus on intergrated solution for beverage and liquid food, such as mineral water, Juice, carbonated beverage, energy drinks, wine, beer, edible oil, dairy and dauily care products, etc.
-
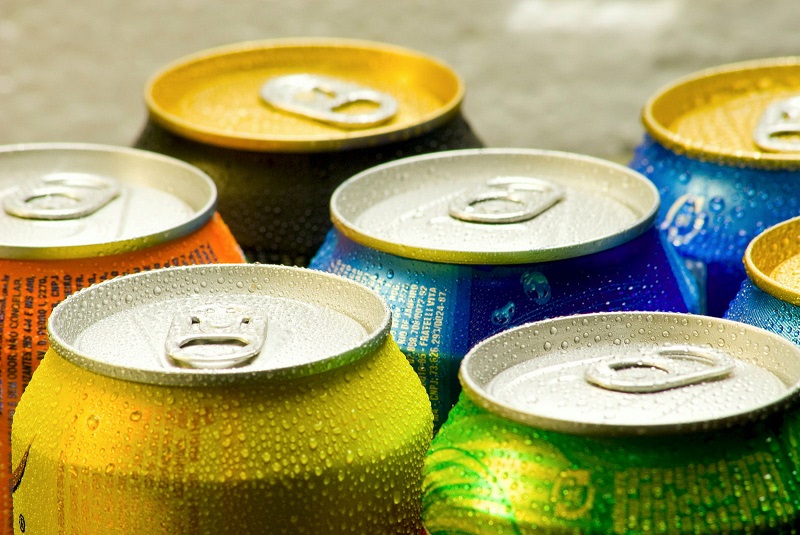

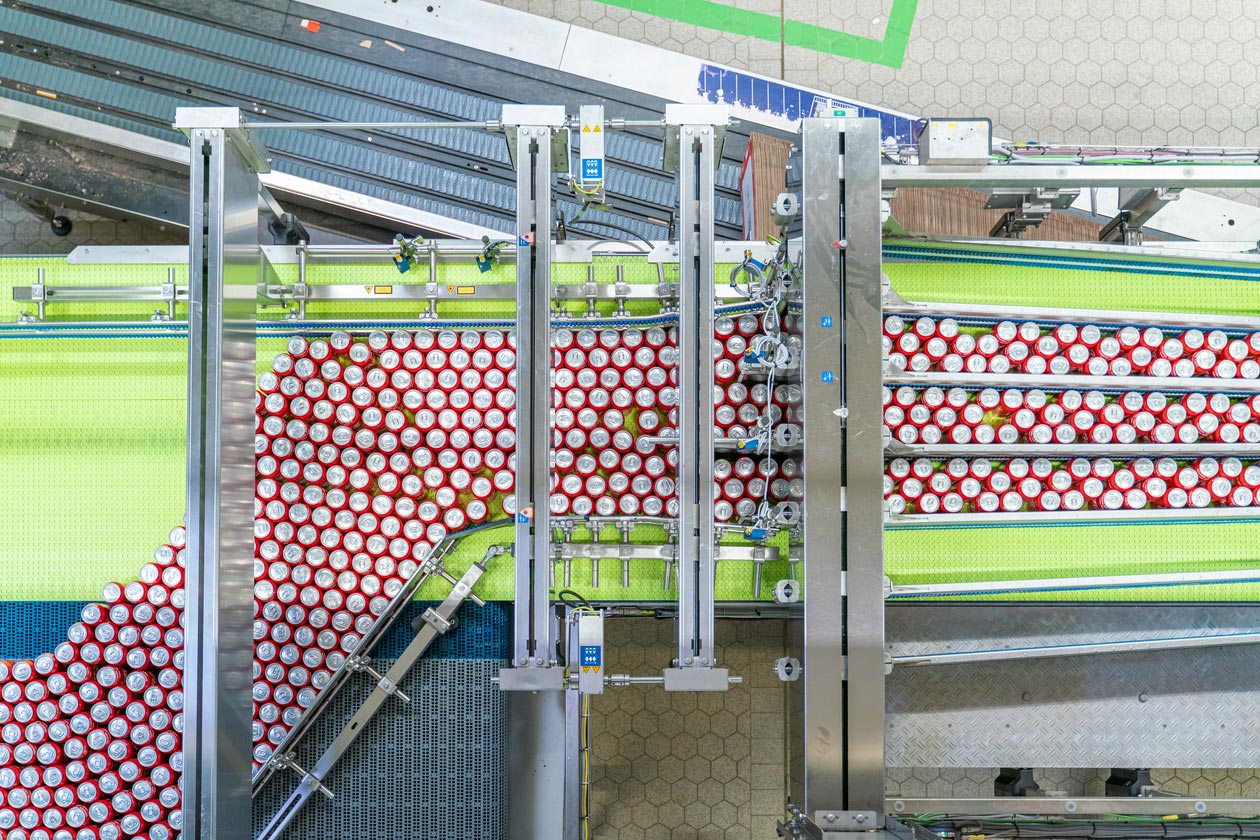
CAN FILLING LINE SOLUTION
Provide solutions for various energy drinks, juice drinks, carbonated beverages, milk, tea, alcohol, and other cans filling

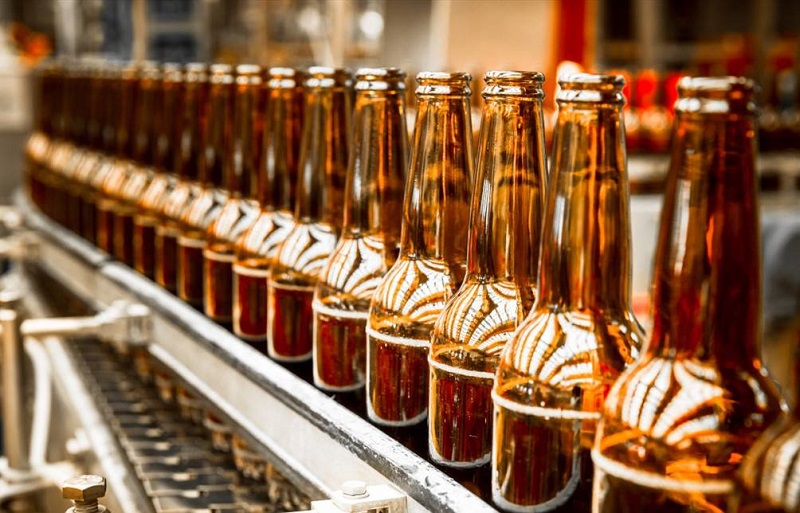
GLASS BOTTLE FILLING LINE SOLUTION
Glass bottle filling line working system is important to know. Bottles driven by variable pitch screw are transferred to rinsing part through bottle-inlet star wheel.

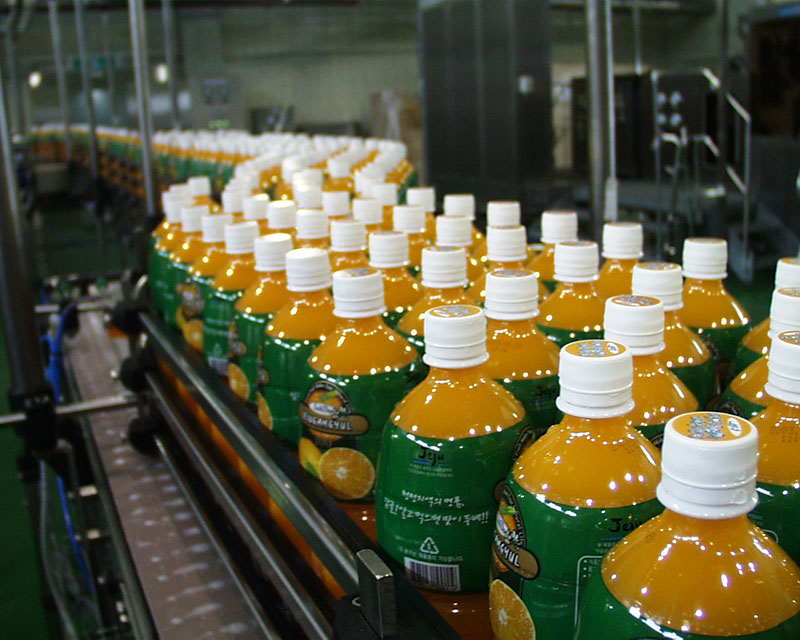
JUICE PRODUCTION LINE SOLUTION
KIWL Machine filling machines will provide different solutions for different products. Every one of your products will have its optional solution.
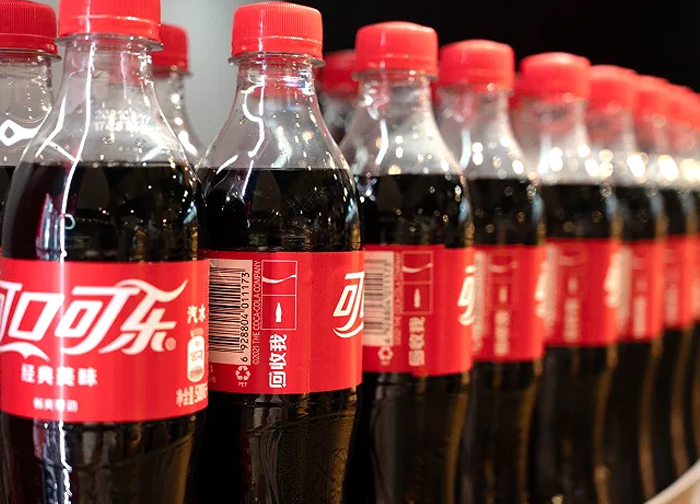

CARBONATED SOFT DRINK PRODUCTION LINE SOLUTION
This Carbonated Soft Drink production line is mainly included beverage mixing system, like sugar melting boiler, double filter, syrup pump,syrup cooling tank, mixing tank, storage tank, etc, also included carbonated drink filling machine, carbonation mixe

WATER FILLING PRODUCTION LINE SOLUTION
KIWL Machine, the expert in liquid product filling, will always provide you with the best solution for your products.

5 GALLON FILLING LINE SOLUTION
This line is mainly used for filling pure water or mineral water of 3 & 5 gallon bottle.
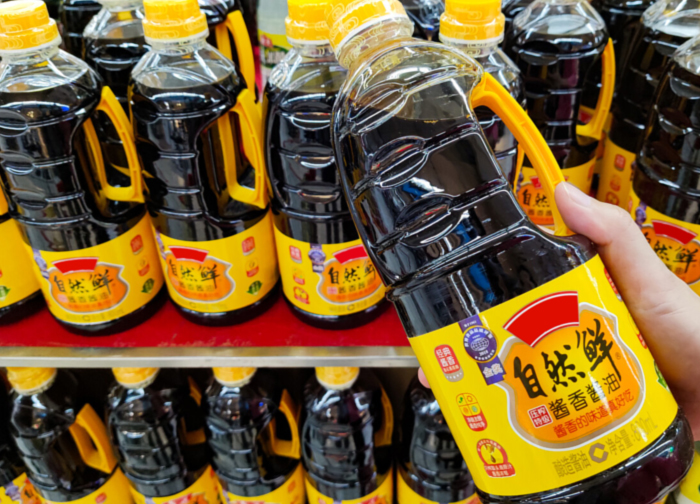

SAUCE JAM PRODUCTION LINE SOLUTION
We use a wide variety of filling valve (Gravity、negative pressure、isobaric、piston type etc.)

Oil PRODUCTION LINE SOLUTION
Oil products include edible oil and industrial oil, like peanut oil, palm oil, blended oil, and lubricating oil etc.
-
-
Cases
-
Cases
We insist on quality first for many years and continue to win customers' trust. Our products are sold all over the world
-

Customer Group Photo
Choose us to choose quality and trust, and provide customers with various needs

Cooperative brands
Choose us to choose quality and trust, and provide customers with various needs
-
-
Video&News
-
Video&News
Welcome to pay attention to and understand us, understand KIWL, understand the dynamics of the beverage machinery industry
-

Video

Company News

Industry News
-
-
Contact
-
Contact
The company is located in Zhangjiagang City, the Yangtze River Delta, bordering Shanghai in the east, Nanjing in the west, Suzhou in the south, and the Yangtze River in the north, with convenient transportation and developed economy.
-

Contacts

Online Message

Company Map
-



